Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
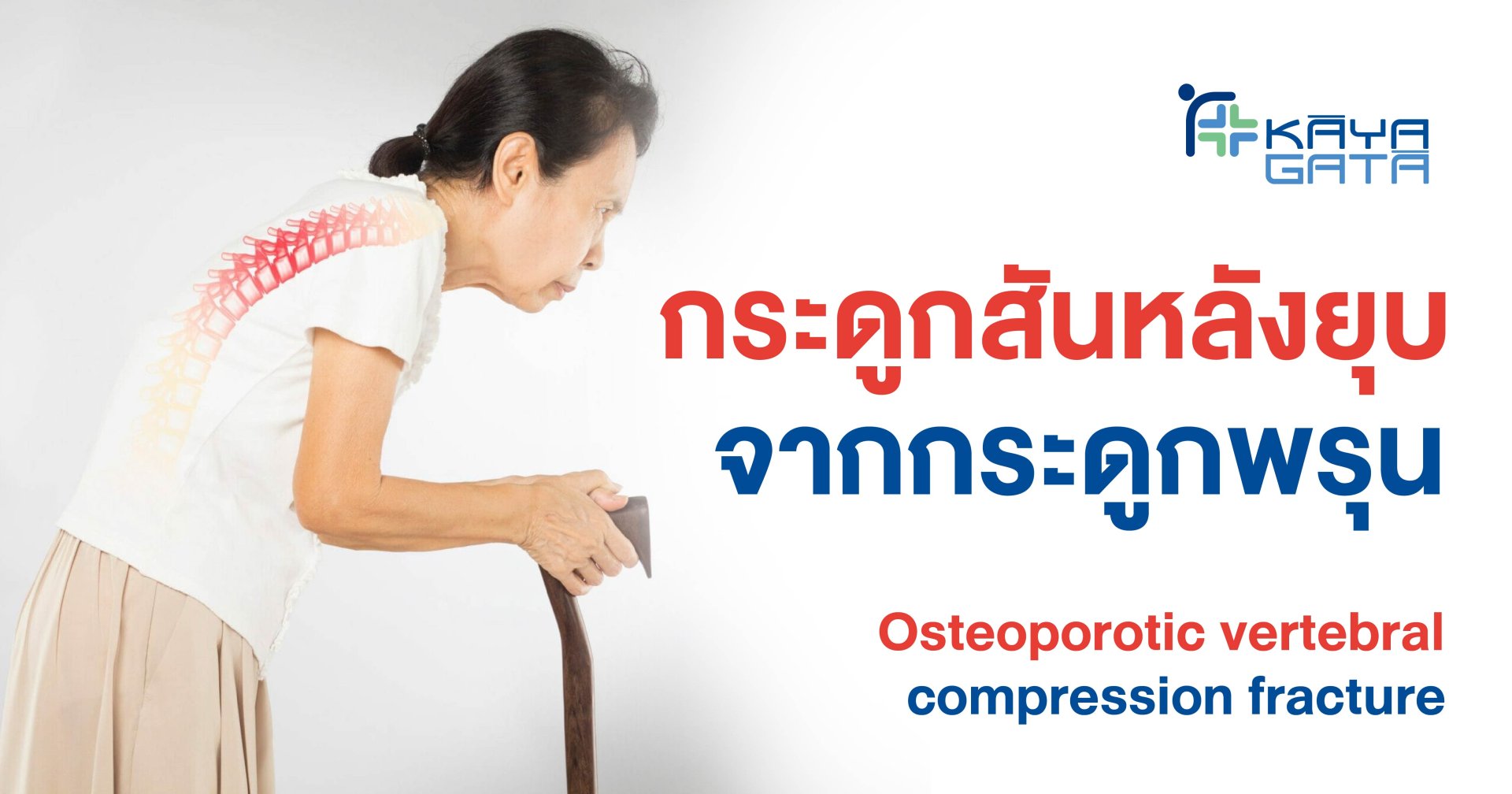
Vertebral Compression from Osteoporosis: A Silent Danger
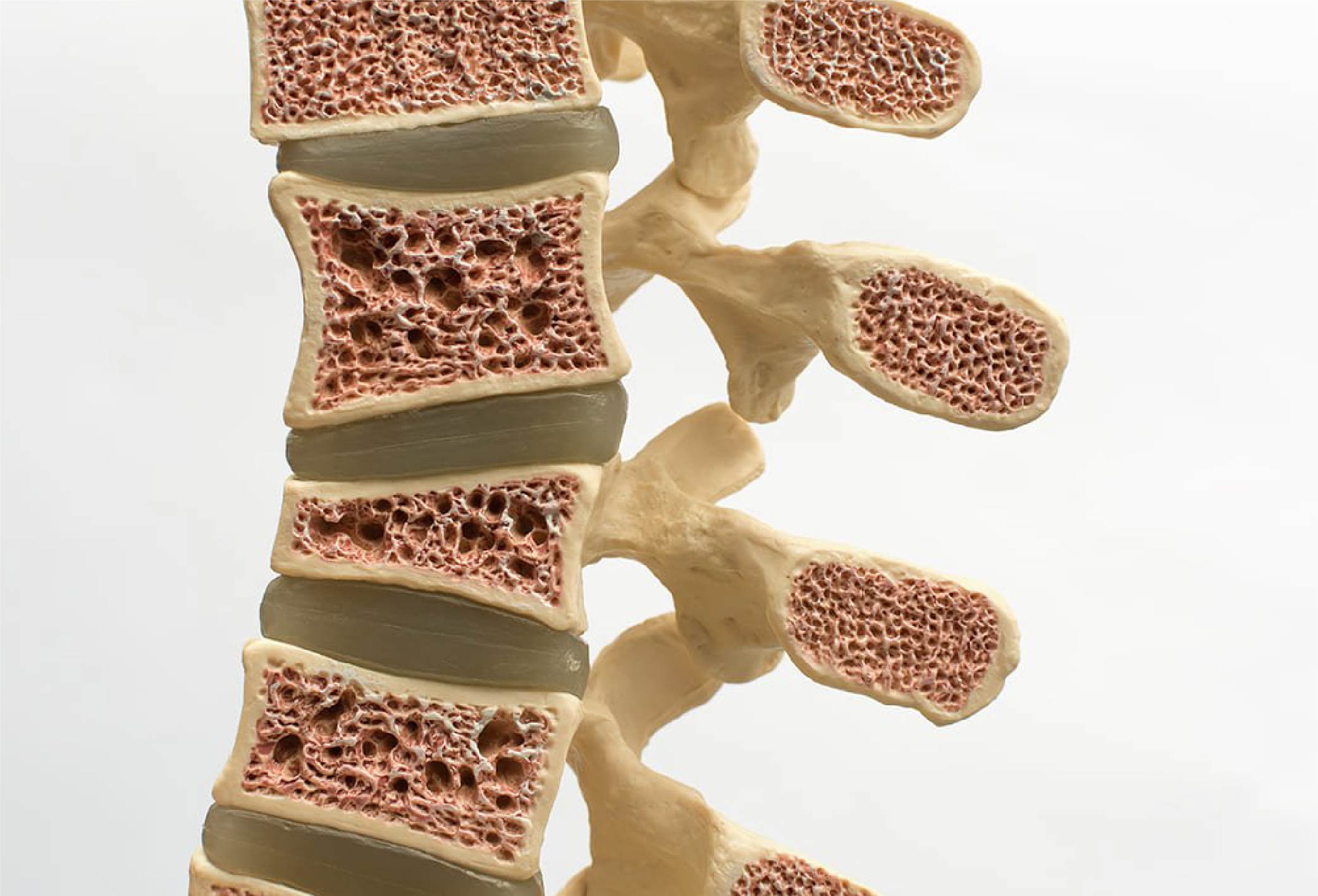
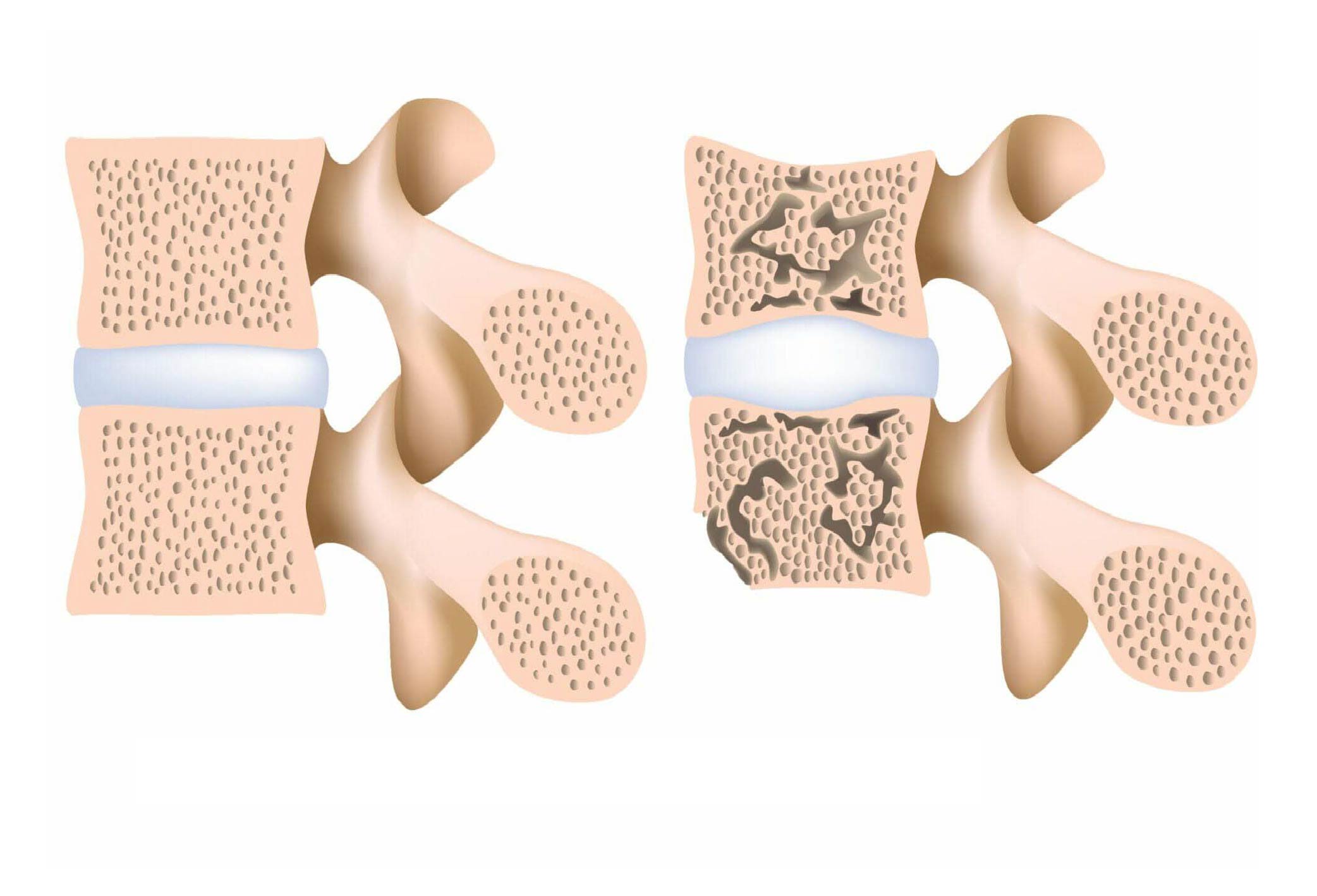
Vertebral compression caused by osteoporosis occurs when weakened spinal bonesdue to decreased bone densitycollapse, fracture, or break under stress.

A Frightening Silent Threat
Older adults are particularly prone to vertebral compression resulting from osteoporosis. This condition is often called a silent disease because it shows no early symptoms. By the time noticeable changes such as a hunched back or loss in height occur, vertebral collapse has often already taken place.
Osteoporosis makes bones fragile and prone to fractures. Other risk factors for developing osteoporosis include:
- Gender Women are more at risk than men
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- High caffeine intake
- Low body weight
- Long-term use of antacids or corticosteroids
Accurate Diagnosis Is Key
When vertebral compression occurs, patients often experience severe back pain, especially during movement. In some cases, nerve compression may also cause numbness or weakness.
A detailed diagnostic process is essential. Physicians will identify the exact location of the vertebral collapse and evaluate its severity. Before beginning treatment, its crucial to understand the goal: physical therapy will not restore the collapsed vertebra, but rather aims to:
- Alleviate pain
- Prevent further collapse
- Support recovery and tissue regeneration
In cases requiring structural correction, more invasive methods like bone cement injection or spinal fusion with screws may be necessary.
Physical Therapy Techniques
Key therapies include:
- Shock Wave Therapy
Reduces pain and stimulates healing by triggering micro-injuries that promote tissue repair. - Peripheral Magnetic Stimulation (PMS)
Relieves nerve-related pain, numbness, and radiating symptoms. It also supports nervous system recovery and encourages tissue healing. - High Power Laser Therapy
Decreases pain and inflammation in muscles and joints, stimulates nerve regeneration, and promotes new bone growth. - Mobility and Posture Guidance
Patients are advised on how to move safely, use support devices if necessary, and strengthen the core and back muscles to reduce strain and improve posture.

Regenerative Cellular Therapies
Additional treatments may include:
- Prolotherapy Injected to trigger a mild inflammatory response that activates the bodys natural healing.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Uses a small amount of the patients own blood, processed to concentrate growth factors and injected into the affected area.
- Biological Peptide (Nucleic Acid) Therapy Stimulates cell repair and regeneration.
- Cell Therapy Uses stem or regenerative cells to repair or replace damaged tissue.
Prevention Is Better Than Cure
Since osteoporosis often has no warning signs, early diagnosis is critical. The best way to protect yourself is through bone density testing. This can help determine the risk of osteoporosis and guide personalized prevention strategies.
If you're already diagnosed, proper lifestyle adjustments and monitoring can prevent complications like vertebral collapse. Dont waittake proactive steps to protect your spine and overall health.
.........................


