Physical Therapy for Hip Osteoarthritis
Understanding a condition that can creep in unnoticedand how to treat it without surgery.
When we hear the term hip osteoarthritis, many assume it's a condition affecting only the elderly. In truth, however, younger individuals can also develop hip osteoarthritis due to various factors.
Hip Osteoarthritis in Younger People
It can occur due to:
- Sports injuries
- Cartilage disorders at the hip joint
- Fractures near the hip caused by accidents, which may lead to degenerative changes later
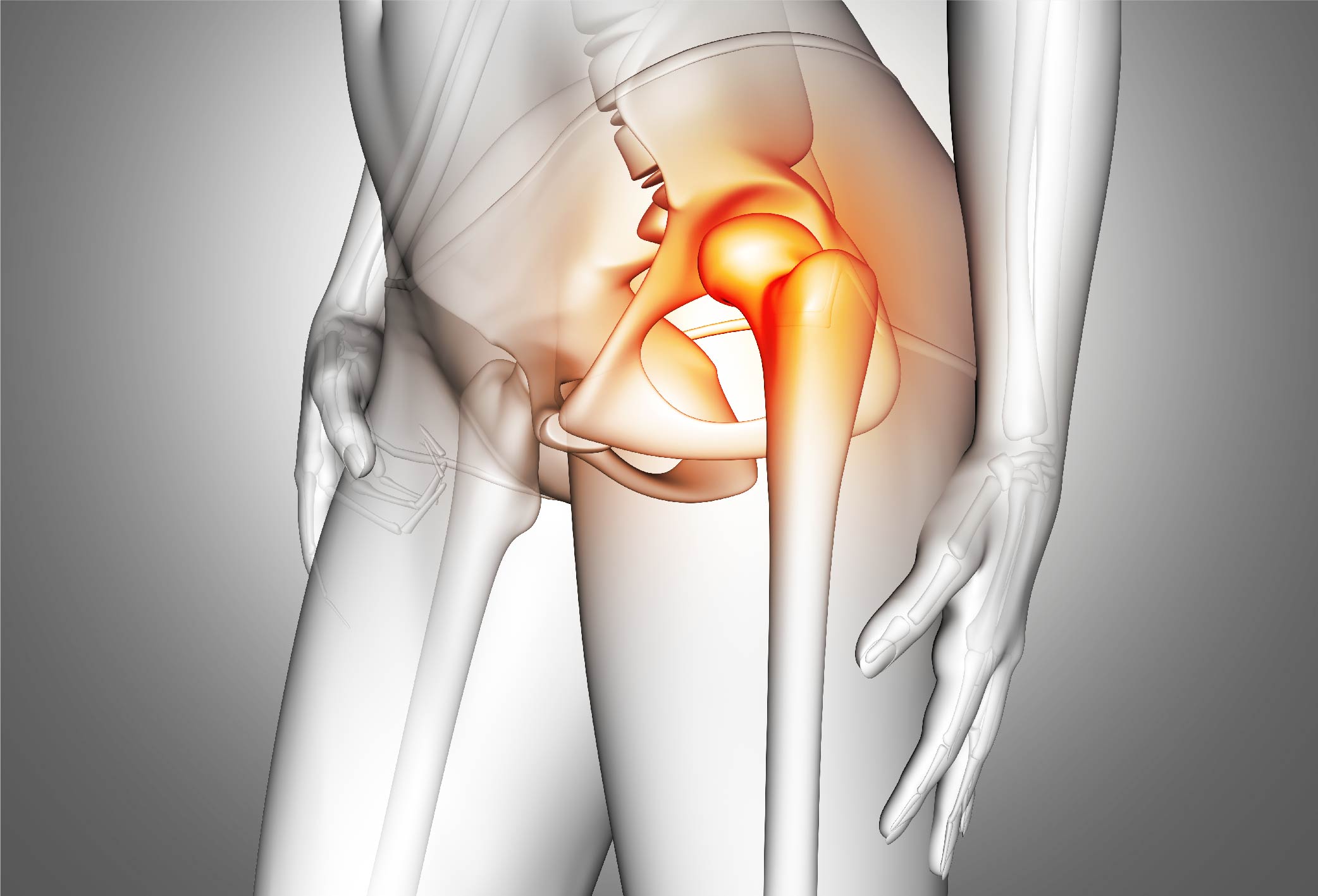
Hip Osteoarthritis in Older Adults
This often results from age-related degeneration and underlying chronic diseases such as:
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
These conditions accelerate cartilage wear. Most patients begin experiencing degeneration around the age of 45 and older. In women, post-menopausal estrogen loss contributes to bone thinning and faster joint deterioration.
Hip and Knee Pain: A Nerve Connection
Hip joint pain often radiates to the knee due to interconnected nerves. Some patients who seek care for knee pain are actually diagnosed with hip degeneration, and vice versa. Therefore, physicians may examine both areasas well as the spineto find the root cause.
Never self-diagnose joint pain. Hip, knee, and spinal pain are often interrelated and require a thorough medical assessment.
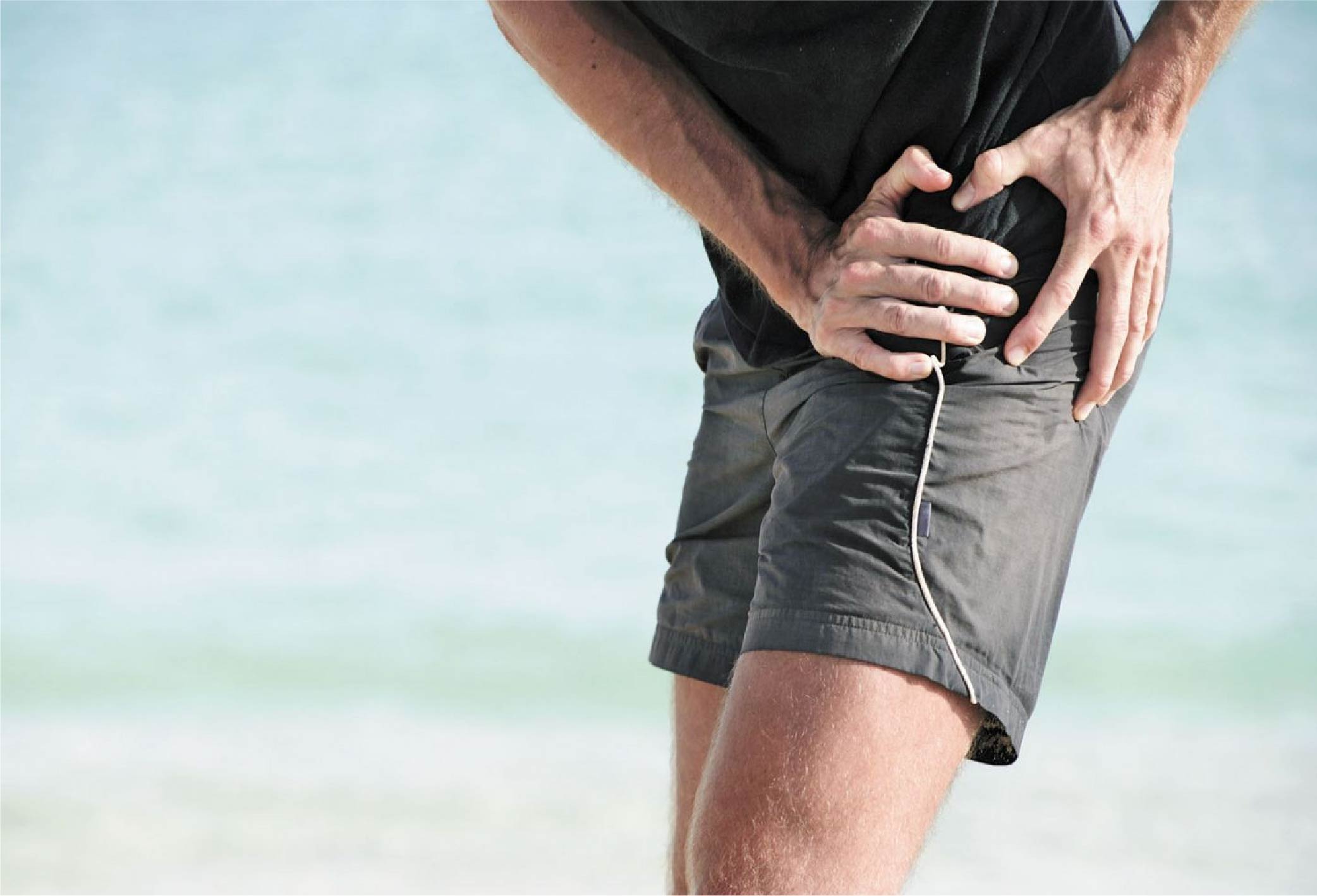

Warning Signs of Hip Osteoarthritis
- Pain in the hip area, sometimes radiating to the buttocks or knees
- A feeling of stiffness or "catching" during movement
- Limited range of motion: difficulty sitting cross-legged or squatting
- Needing support when climbing stairs
Early Intervention Brings Better Outcomes
Hip osteoarthritis can be treated through various methods. At Gaikata, physical therapy is a primary approachalongside cellular-level regenerationto manage and even reverse early-stage degeneration.
Will Physical Therapy Cure My Hip Osteoarthritis?
It depends on the severity:
- If degeneration is below 75%, conservative treatment including physical therapy and cellular repair can be highly effective.
- If degeneration exceeds 75%, joint replacement surgery may be required.
Early diagnosis and treatment can slow or even prevent the need for surgery altogether.
Physical Therapy Options
- Peripheral Magnetic Stimulation (PMS):
Reduces pain and numbness, improves circulation, and promotes nerve and tissue regeneration - High-Power Laser Therapy:
Relieves muscle and joint pain, encourages deep tissue and nerve healing without heating or damaging the skin - Shock Wave Therapy:
Stimulates blood flow and natural tissue repair while reducing inflammation at the pain site

Cellular-Level Regenerative Therapies
In addition to physical therapy, Gaikata offers treatments that nourish, repair, and regenerate hip cartilage and connective tissues:
- Prolotherapy
- PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma)
- Bioactive Peptide (Nucleic Acid) Injections
- Cell-Based Regenerative Therapy
Patients also receive personalized nutritional counseling, vitamin supplementation, and lifestyle advice to support healing.

Safe Exercise Guidance
If you're accustomed to regular physical activity, always consult your doctor first. If approved, exercise only with techniques recommended by a physical therapistand always avoid pain-inducing movements. Pushing through pain can worsen cartilage damage.
Take Charge of Your Hip Health
Hip osteoarthritis is manageableespecially if addressed early. Paying attention to early symptoms, adopting healthier behaviors, and opening yourself to consistent, focused treatment is key.
Think of caring for your health as an investmentnot just financially, but in time and effort. The return? A stronger, pain-free body and better quality of life.
.................................


